Cloud Storage Config
Captain supports indexing from both Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage buckets.
This guide walks through the process of connecting them with Captain.
Choose your cloud storage provider
AWS S3 Bucket Setup
Step 1: Create the Bucket
-
Log in to the AWS Console
-
Navigate to S3 → Buckets → Create bucket
Captain recommends the following standard configuration:- Select a region for the bucket
- Set a bucket name
- Keep General Purpose Storage selected if asked
- Keep ACLs disabled
- Keep Block all public access checked
- (Optional) Enable Bucket Versioning (for SOC 2 compliance)
- Once these settings are configured, the bucket is ready.
Scroll down and click Create bucket
AWS S3 Access Keys
To index files from Amazon S3 buckets, you’ll need an AWS Access Key ID and Secret Access Key.
Step 1: Navigate to IAM Security Credentials
- Log in to the AWS Console
- Click on your account name in the top-right corner
- Select Security credentials from the dropdown menu
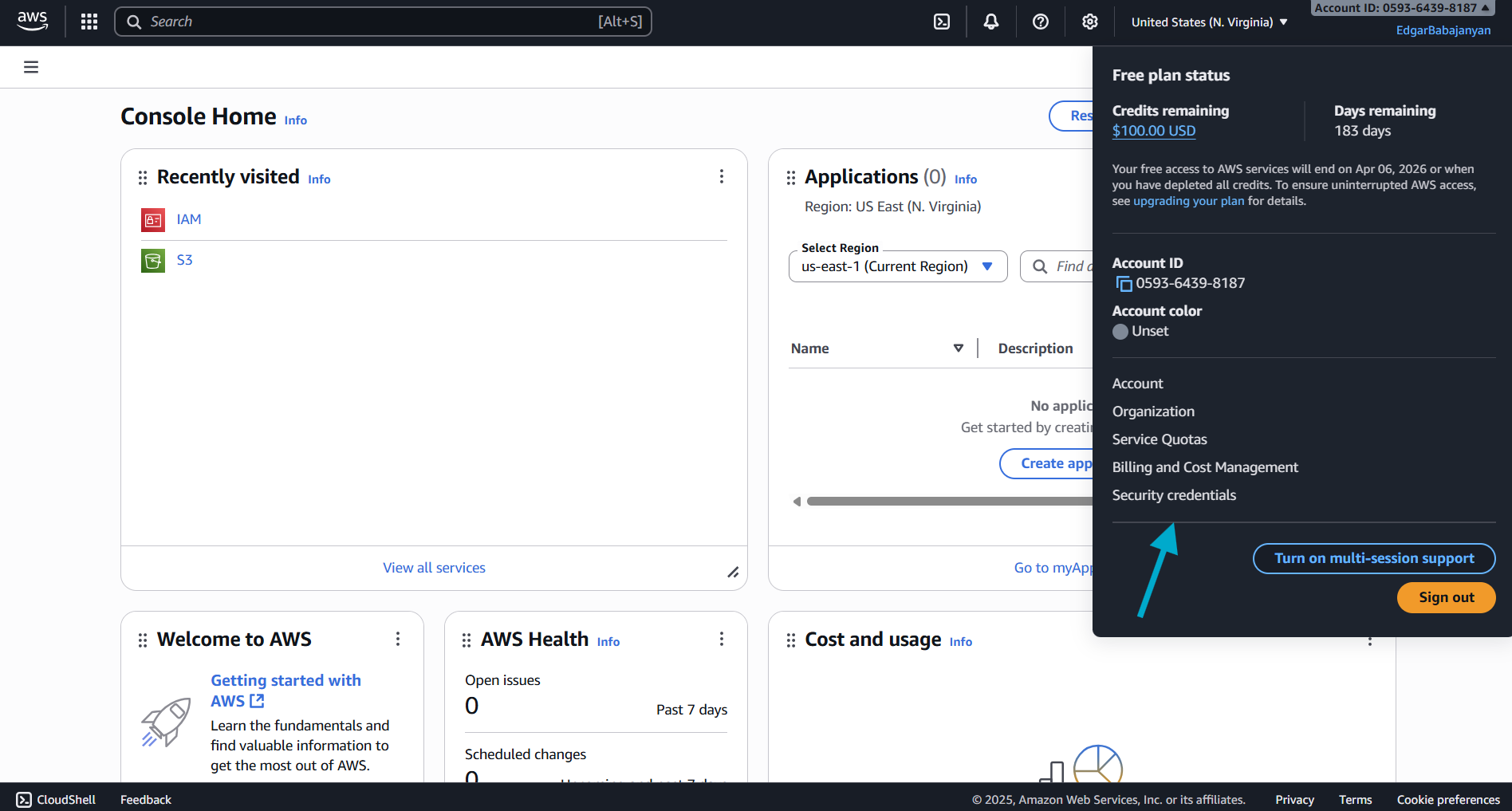
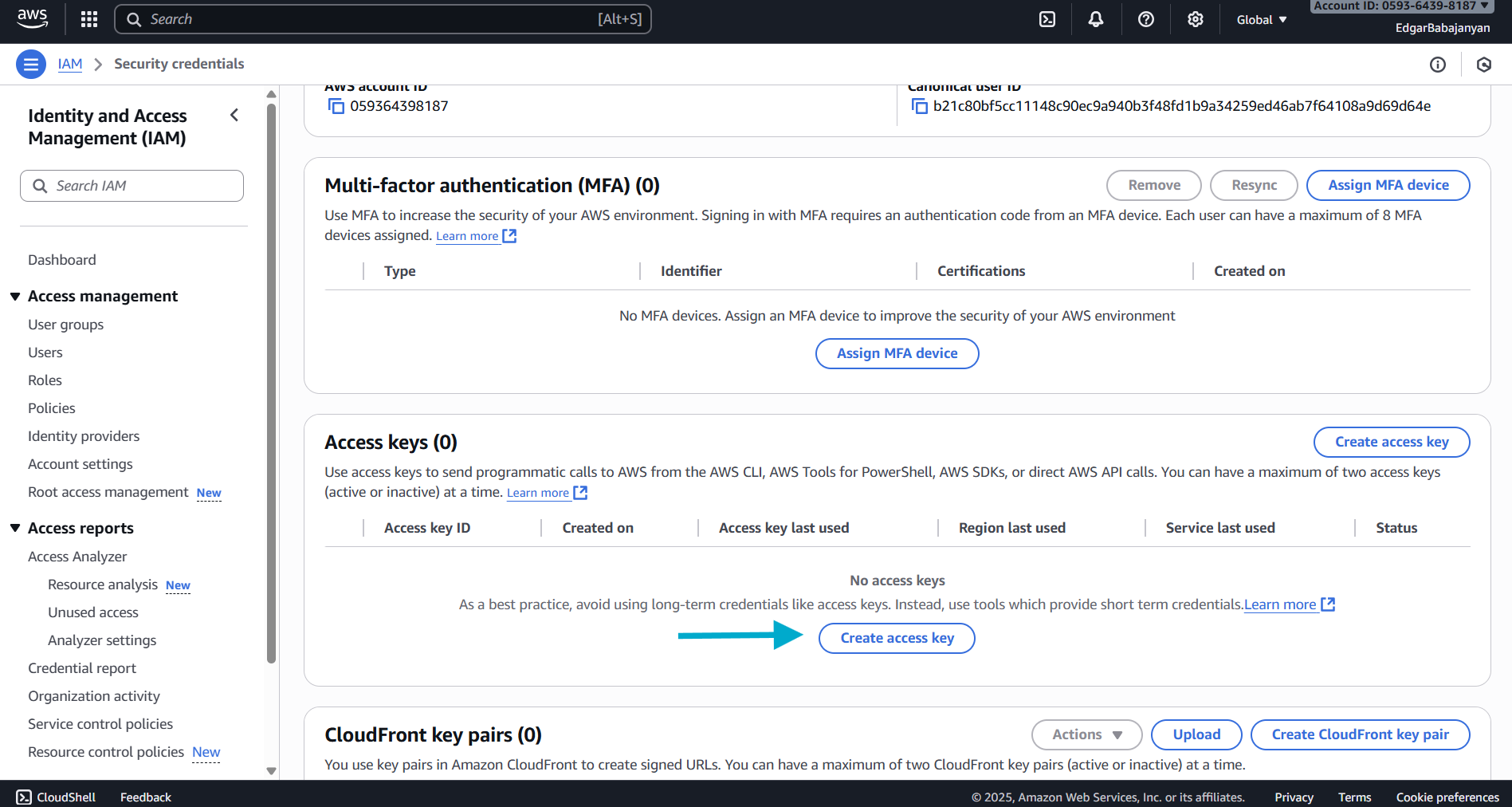
Step 2: Create Access Key
- Scroll down to the Access keys section
- Click the Create access key button
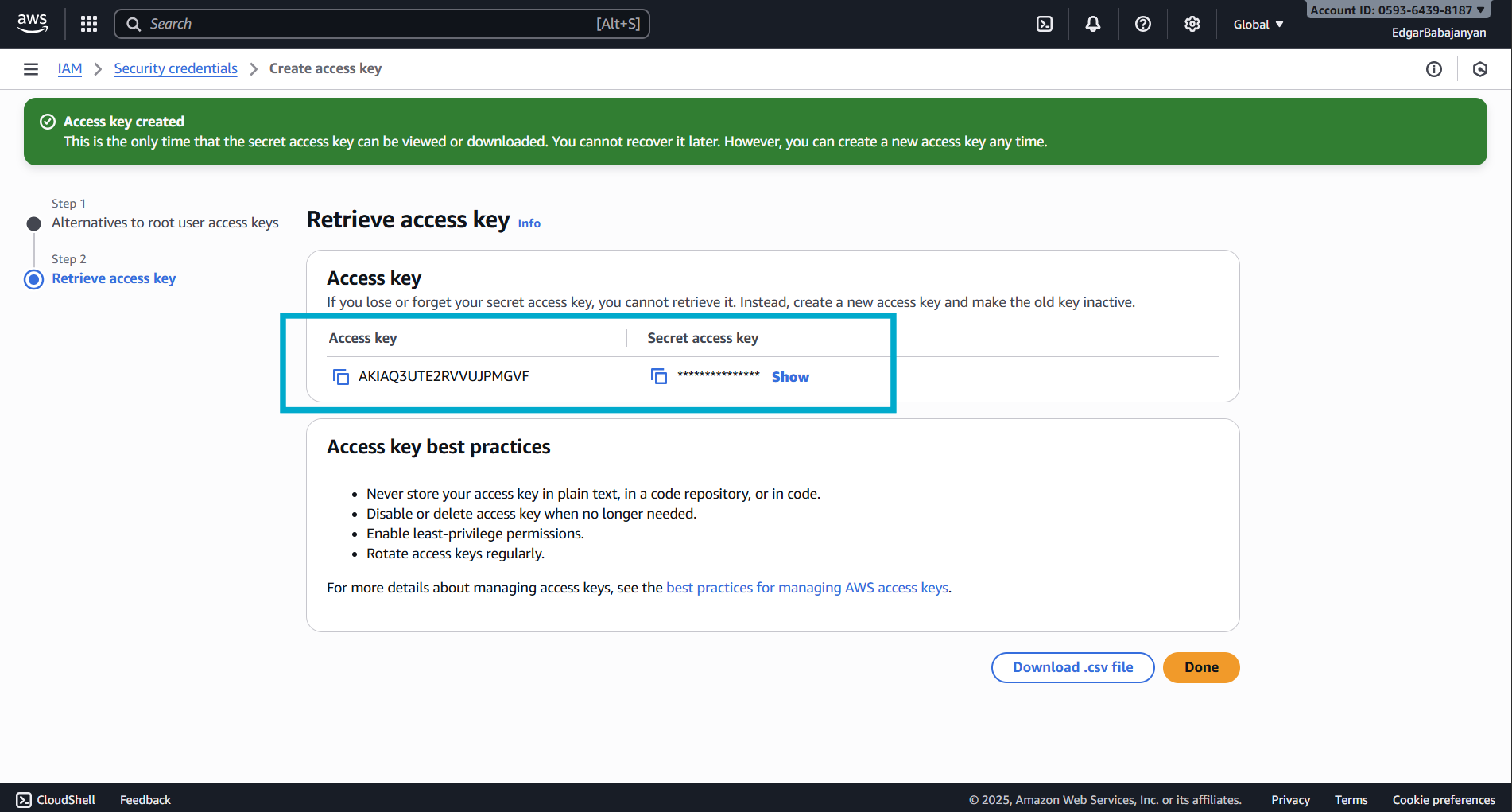
Step 3: Retrieve Your Credentials
- Your Access Key ID and Secret Access Key will be displayed
- Important: This is the only time you can view the Secret Access Key
- Click Show to reveal the Secret Access Key
- Copy both the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key to a secure location
- Optionally, download the
.csvfile for safekeeping
Required IAM Permissions (AWS)
Your AWS access key needs the following permissions to work with Captain:
For read-only access to S3 buckets:
Replace your-bucket-name with your actual S3 bucket name.
Google Cloud Storage Bucket Setup
Step 1: Create the Bucket
- Go to Google Cloud Console
- Navigate to Cloud Storage → Buckets → Create
- Enter a unique bucket name (e.g.,
company-captain-documents) - Select a Location type (Region, Dual-region, or Multi-region)
- Select Standard storage class for general use
- Under Access control, select “Uniform” (recommended)
- Click Create
Google Cloud Storage Credentials
To index files from Google Cloud Storage buckets, you’ll need a Service Account JSON key.
Step 1: Navigate to Service Accounts
- Go to Google Cloud Console
- Navigate to IAM & Admin → Service Accounts
- Click Create Service Account
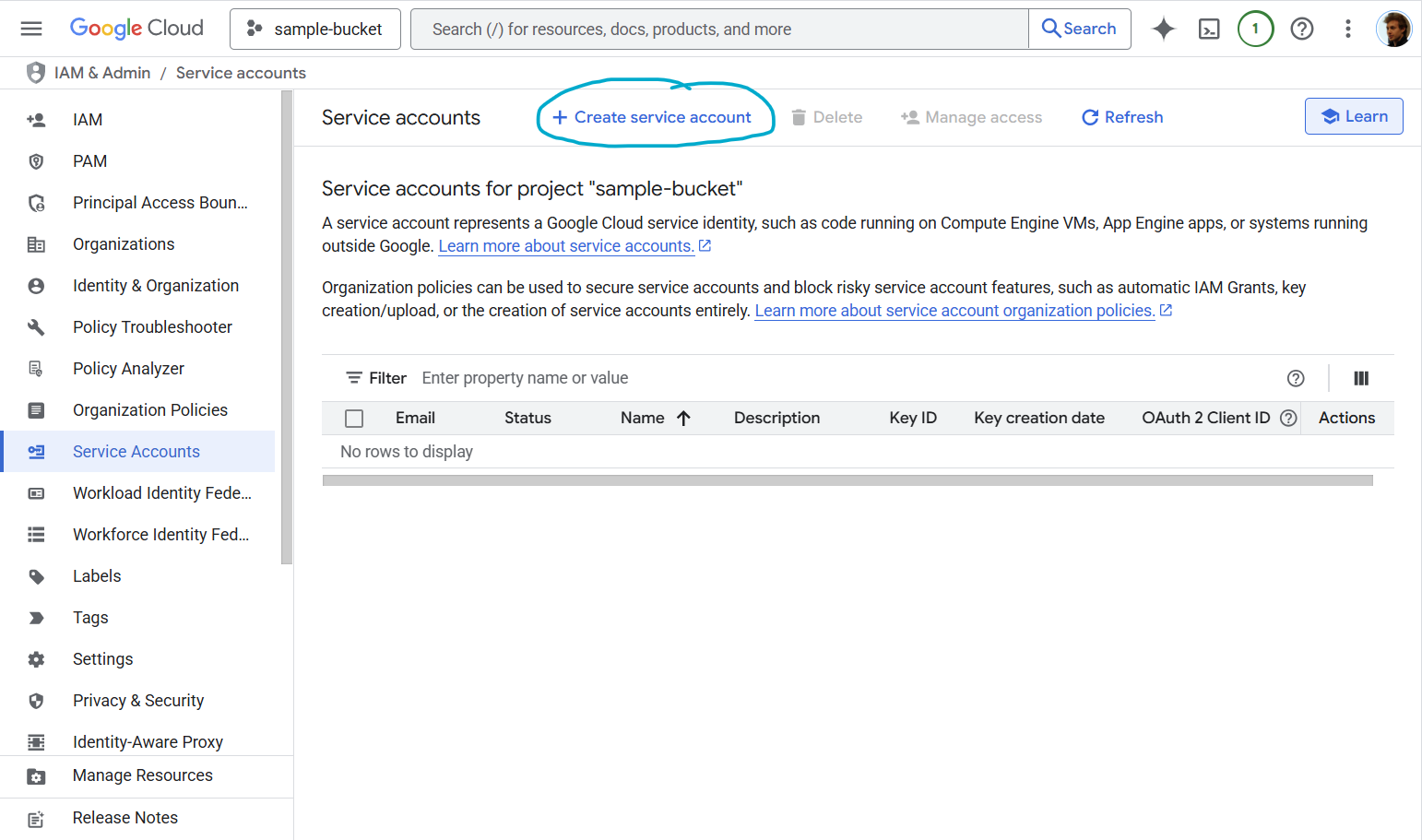
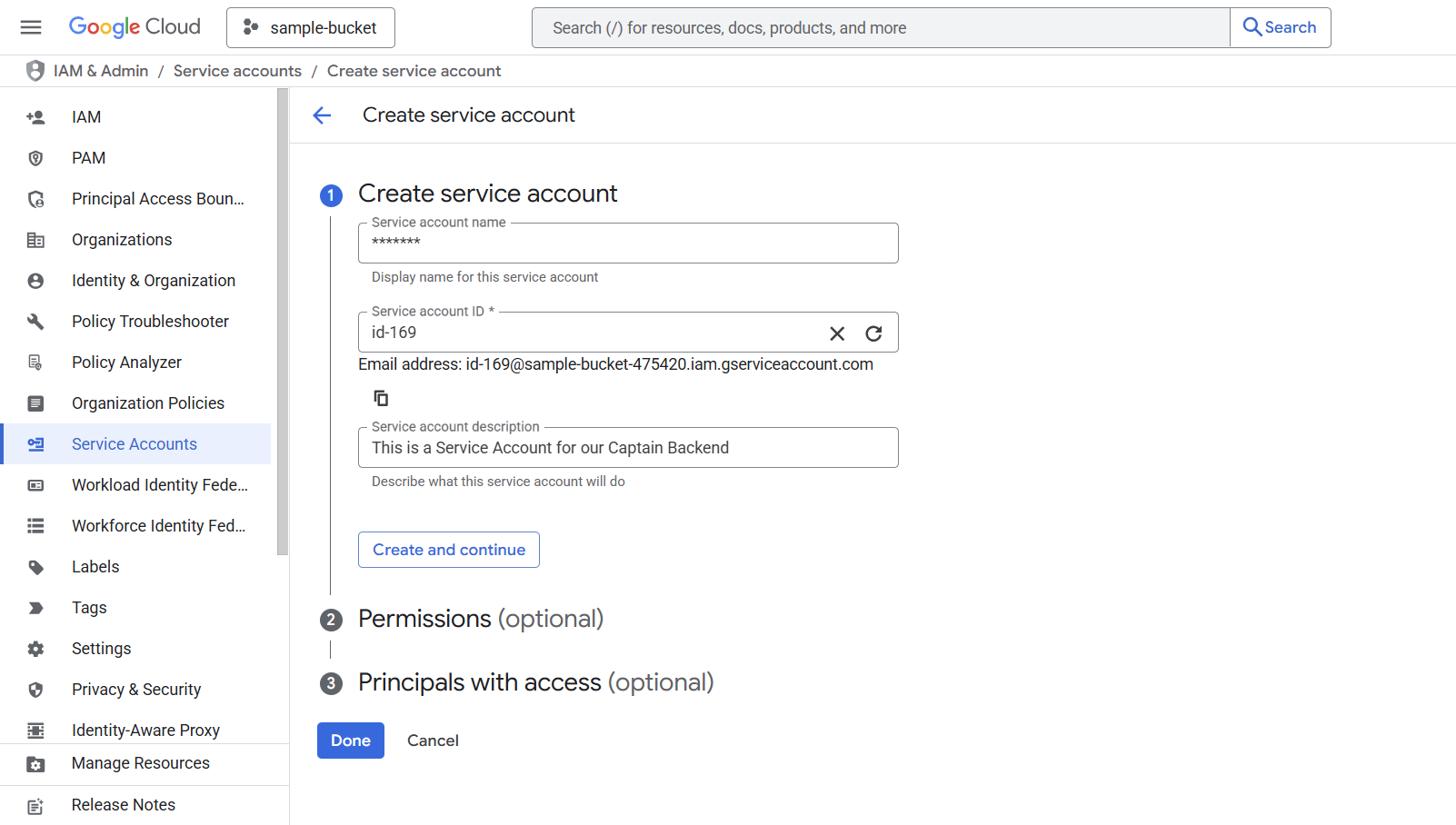
Step 2: Create Service Account
- Enter a Service account name (e.g.,
captain-storage-access) - Add a Service account description (optional but recommended)
- The Service account ID will be auto-generated
- Click Create and continue
Step 3: Grant Permissions
Under Grant this service account access to project, choose the appropriate role based on your needs:
For read-only access to buckets/objects:
- Role: Storage Object Viewer (
roles/storage.objectViewer)
For read/write access:
- Role: Storage Object Admin (
roles/storage.objectAdmin)
For full bucket management:
- Role: Storage Admin (
roles/storage.admin)
Click Continue → Done
Step 4: Create and Download JSON Key
- You’ll now see your new service account in the list
- Click on the service account name
- Navigate to the Keys tab
- Click Add Key → Create New Key
- Select JSON as the key type
- Click Create
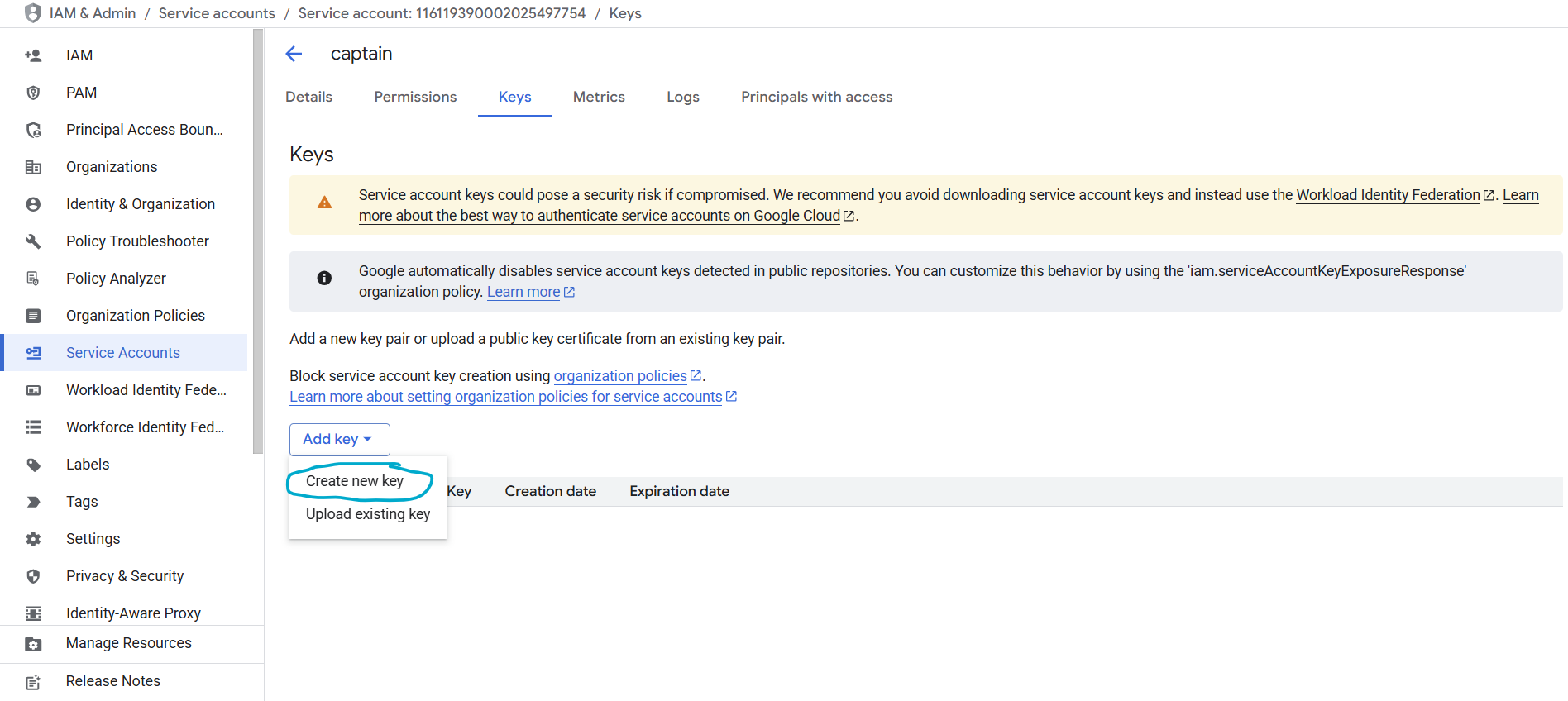
The JSON key file will automatically download to your computer. This file contains your service account credentials.
JSON Key File Format
Your downloaded JSON key will look like this:
Using Google Cloud Service Accounts with Captain
Store the JSON key file securely (e.g., in a secret management service or as an environment variable)
Troubleshooting
AWS Issues
Error: “Invalid AWS credentials”
- Verify your Access Key ID and Secret Access Key are correct
- Check that the access key is active in the IAM console
- Ensure your IAM user/role has the necessary S3 permissions
Error: “Access Denied”
- Verify your IAM permissions include
s3:GetObjectands3:ListBucket - Check bucket policies and ensure they allow your IAM user/role
- Verify the bucket region matches the
bucket_regionparameter
Google Cloud Issues
Error: “Invalid service account credentials”
- Verify the JSON key file is valid and not corrupted
- Check that the service account is enabled
- Ensure the service account has the necessary Storage permissions
Error: “Permission denied”
- Verify the service account has the appropriate Storage role
- Check that the bucket exists and the service account has access
- Review IAM permissions in the Google Cloud Console
Need Help?
If you encounter issues obtaining or using your cloud storage credentials, contact Captain support:
- Email: support@runcaptain.com

